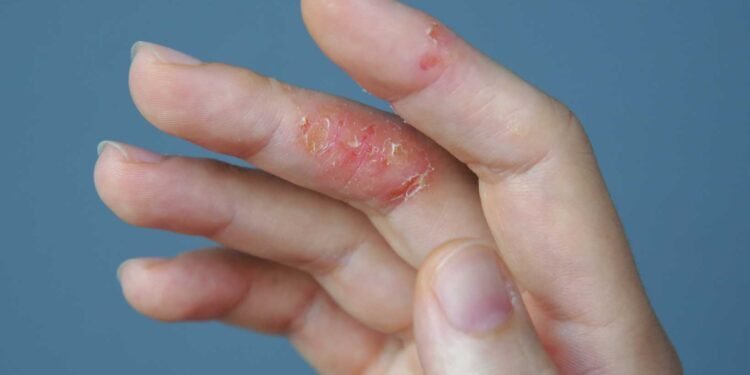
Mold is a common allergen that can cause a variety of health issues, including skin conditions like eczema. Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, itching, and inflammation. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, research suggests that it may be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. One of these environmental factors could be mold.

Understanding Eczema and Its Triggers
Eczema is a complex condition that can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, allergens, and irritants. Mold is one of these triggers, as exposure to mold can cause an allergic reaction that can aggravate eczema symptoms. In addition, mold can also cause respiratory issues that can make it more difficult to manage eczema symptoms.
Mold Allergies and Eczema
Mold allergies are a common trigger for eczema, as exposure to mold spores can cause an allergic reaction that can worsen eczema symptoms. Symptoms of mold allergies can include sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and skin rashes. If you suspect that mold may be triggering your eczema symptoms, it’s important to speak with your doctor to determine the best course of treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Eczema is a complex condition that can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, allergens, and irritants.
- Exposure to mold can cause an allergic reaction that can aggravate eczema symptoms.
- If you suspect that mold may be triggering your eczema symptoms, it’s important to speak with your doctor to determine the best course of treatment.
Understanding Eczema and Its Triggers
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed skin. Eczema can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental triggers, and an overactive immune system. In some cases, eczema symptoms can be aggravated by mold exposure.
The Role of the Immune System in Eczema
The immune system plays a significant role in the development of eczema. People with eczema have an overactive immune system that responds to harmless substances as if they were harmful. This overreaction causes inflammation and irritation, leading to the characteristic symptoms of eczema.
Common Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers can also play a role in the development and exacerbation of eczema symptoms. Common environmental triggers include:
-
Mold: Mold is a common environmental allergen that can trigger eczema symptoms in some people. Mold spores can be found in damp areas of the home, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
-
Pollen: Pollen is a common allergen that can trigger eczema symptoms in some people. Pollen is most prevalent in the spring and summer months.
-
Dust mites: Dust mites are tiny insects that can trigger eczema symptoms in some people. They are commonly found in bedding, carpets, and upholstered furniture.
-
Pet dander: Pet dander is a common allergen that can trigger eczema symptoms in some people. It is found in the skin, hair, and saliva of pets.
Avoiding these environmental triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of eczema symptoms. It is important to note that not all triggers will affect every person with eczema, and triggers can vary from person to person.
Mold Allergies and Eczema
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, studies have shown that mold exposure can aggravate eczema symptoms in some people. In this section, we will explore the connection between mold allergies and eczema.
Identifying Mold Allergy Symptoms
Mold allergy symptoms can vary from person to person. In some cases, people may not experience any symptoms at all. However, some common symptoms of mold allergy include:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Cough and postnasal drip
- Itchy eyes, nose, and throat
- Watery eyes
- Dry, scaly skin
If you have eczema and experience any of these symptoms, it may be worth considering if mold exposure could be contributing to your eczema flare-ups.
The Connection Between Mold Exposure and Eczema Flare-Ups
Studies have shown that mold exposure can aggravate eczema symptoms in some people. One study found that children who were exposed to mold in their homes were more likely to develop eczema than children who were not exposed to mold. Another study found that people with eczema who were exposed to mold had more severe eczema symptoms than those who were not exposed to mold.
The exact mechanism behind this connection is not fully understood. However, it is thought that mold exposure can trigger an immune response in some people, which can lead to eczema flare-ups.
If you have eczema and suspect that mold exposure may be aggravating your symptoms, it is important to take steps to reduce your exposure to mold. This may include keeping your home dry and well-ventilated, using a dehumidifier, and avoiding damp areas such as basements and bathrooms.
In conclusion, while the exact cause of eczema is unknown, mold exposure can aggravate eczema symptoms in some people. If you have eczema and suspect that mold exposure may be contributing to your symptoms, it is important to take steps to reduce your exposure to mold.
Diagnosing Mold-Related Health Issues

Mold allergies and eczema can have similar symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose the root cause of the problem. However, if you suspect that your eczema symptoms are caused or aggravated by mold exposure, it’s important to seek medical attention to get a proper diagnosis.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent eczema symptoms that do not improve with over-the-counter medications or home remedies, it’s time to see a doctor. A dermatologist can examine your skin and help determine if mold exposure is causing or contributing to your eczema symptoms.
Tests for Mold Allergy and Eczema
To diagnose mold allergy, your doctor may recommend a skin prick test or a blood test. A skin prick test involves pricking the skin with a tiny amount of mold allergen and observing the reaction. A blood test can measure the level of antibodies in your blood that are produced in response to mold exposure.
To diagnose eczema, your doctor may perform a physical examination of your skin and ask about your medical history. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
If mold exposure is suspected, your doctor may recommend additional tests to confirm the presence of mold in your environment. These tests may include air or surface samples that are analyzed in a laboratory for the presence of mold spores.
Overall, it’s important to work with a doctor to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for mold-related health issues. With proper care, it’s possible to manage eczema symptoms and reduce the impact of mold exposure on your health.
Mold Growth and Indoor Air Quality

Mold growth is a common problem in many homes, and it can have a significant impact on indoor air quality. Mold spores are airborne and can cause a range of health problems, including respiratory issues and skin irritation. In this section, we will explore the high-risk areas for mold in the home and the effects of mold spores on health.
High-Risk Areas for Mold in the Home
Mold thrives in areas with high humidity and moisture, making bathrooms, kitchens, and basements prime locations for mold growth. In the bathroom, mold can grow in the shower, around the sink, and on the walls and ceiling. In the kitchen, mold can grow on food, in the sink, and on the walls and ceiling. In the basement, mold can grow on walls, floors, and ceilings.
To prevent mold growth, it is important to keep these areas dry and well-ventilated. This can be achieved by using exhaust fans, dehumidifiers, and opening windows. Regular cleaning and maintenance can also help prevent mold growth.
Effects of Mold Spores on Health
Airborne mold spores can cause a range of health problems, particularly in individuals with respiratory issues or allergies. Exposure to mold spores can cause symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, and skin irritation. In some cases, exposure to mold spores can lead to more serious health problems, such as asthma attacks.
To reduce the risk of health problems caused by mold spores, it is important to maintain good indoor air quality. This can be achieved by keeping humidity levels below 60%, using air purifiers, and regularly cleaning and maintaining the home. If mold is suspected, it is important to address the issue promptly by identifying and eliminating the source of the mold growth.
In summary, mold growth can have a significant impact on indoor air quality and can cause a range of health problems. By identifying high-risk areas for mold growth and taking steps to prevent and eliminate mold growth, individuals can maintain good indoor air quality and reduce the risk of health problems caused by mold spores.
Treatment and Management
Medical Treatments for Eczema and Mold Allergies
If you suspect that mold is causing or aggravating your eczema symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medication to help manage your eczema symptoms, such as corticosteroid creams or ointments. These medications can help reduce inflammation and itching, and improve the appearance of your skin.
In addition, if you are experiencing mold allergies, your healthcare provider may recommend antihistamines to help manage your symptoms. Antihistamines work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by your immune system in response to allergens like mold.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, there are several home remedies and lifestyle changes that you can make to help manage your eczema symptoms and reduce your exposure to mold.
First and foremost, it is important to keep your skin moisturized. Using a moisturizer can help prevent dryness and itching, which can worsen your eczema symptoms. Look for a moisturizer that is fragrance-free and hypoallergenic.
It is also important to avoid exposure to mold as much as possible. This may mean taking steps to reduce the humidity in your home, such as using a dehumidifier or fixing any leaks or water damage. You may also need to take steps to remove mold from your home, such as cleaning moldy surfaces with a solution of bleach and water.
In addition, it is important to avoid scratching your skin, as this can worsen your eczema symptoms and increase your risk of infection. You may need to take steps to reduce stress and anxiety, as these can also worsen your eczema symptoms.
Overall, there are several medical treatments, home remedies, and lifestyle changes that can help manage your eczema symptoms and reduce your exposure to mold. If you are experiencing eczema symptoms and suspect that mold may be a contributing factor, it is important to seek medical attention and take steps to reduce your exposure to mold.
Preventing Mold in Your Environment

Mold can be a trigger for eczema symptoms. Therefore, it is important to take measures to prevent mold growth in your environment. The following are some tips to help prevent mold growth:
Humidity Control and Ventilation
One of the most important steps in preventing mold growth is to control humidity levels in your home. High humidity levels can create a breeding ground for mold. The ideal humidity level is between 30-50%. You can use a dehumidifier to control humidity levels in your home. It is important to keep the dehumidifier clean and well-maintained to prevent mold growth inside the unit.
Proper ventilation is also important in preventing mold growth. Make sure that your home is properly ventilated, especially in areas like the bathroom and kitchen where moisture levels can be high. Use exhaust fans or open windows to increase airflow and reduce humidity levels.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Regular cleaning and maintenance can also help prevent mold growth. Here are some tips:
- Clean up spills and leaks immediately to prevent moisture accumulation.
- Use mold-resistant paint in areas that are prone to moisture, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
- Clean and maintain air conditioning units, including the filters, to prevent mold growth.
- Use HEPA filters in your air purifiers to remove mold spores from the air.
- Inspect your home regularly for signs of mold growth, such as musty odors, discoloration, or water stains. If you find any signs of mold growth, take immediate action to remove it.
By following these tips, you can help prevent mold growth in your environment and reduce the risk of eczema flare-ups.
Complications and Coexisting Conditions
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that can cause a range of symptoms, including itching, redness, and dryness. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, research has suggested that mold exposure may be a contributing factor for some people. Mold is a type of fungus that can grow in damp environments, and it can release spores into the air that can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals.
Asthma and Respiratory Issues
One of the most common complications of eczema is asthma. According to the Mayo Clinic, many people with eczema develop asthma and hay fever. This can happen before or after developing eczema. Mold exposure is also a known trigger for asthma symptoms, and people with eczema who are exposed to mold may be at an increased risk of developing asthma or experiencing asthma attacks.
In addition to asthma, mold exposure can also cause other respiratory issues, such as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. ABPA is a rare condition that occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to mold spores in the lungs, leading to inflammation and damage. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is another rare condition that can occur when the lungs become inflamed due to exposure to mold spores and other environmental allergens.
Other Allergies and Skin Conditions
People with eczema may also be at an increased risk of developing other allergies and skin conditions. According to Healthline, eczema raises the risk of skin infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. Mold exposure can also increase the risk of skin infections, as well as exacerbate symptoms of eczema.
In addition to skin infections, people with eczema may also be more likely to develop contact dermatitis, which occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. Mold exposure can also cause contact dermatitis, as mold spores can come into contact with the skin and cause an allergic reaction.
Overall, while the link between eczema and mold exposure is not yet fully understood, it is clear that mold exposure can exacerbate symptoms of eczema and increase the risk of complications and coexisting conditions. It is important for individuals with eczema to take steps to reduce their exposure to mold, such as keeping their home dry and well-ventilated, using air purifiers, and avoiding damp environments.
Understanding and Addressing Psychological Impacts
Living with eczema can be challenging, and it is not just the physical symptoms that can cause distress. Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression can significantly impact the quality of life of individuals with eczema. In this section, we will explore the relationship between psychological impacts and eczema, and offer some tips for addressing these issues.
Stress and Eczema
Stress is a common trigger for eczema flare-ups. When the body is under stress, it releases hormones such as cortisol, which can cause inflammation and exacerbate eczema symptoms. In addition, stress can lead to increased scratching, which can damage the skin and worsen eczema.
To manage stress, individuals with eczema may benefit from relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. They may also find it helpful to identify and avoid triggers that cause stress, such as certain foods or activities. Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can also be beneficial.
The Emotional Toll of Chronic Conditions
Living with a chronic condition like eczema can take a toll on mental health. Individuals with eczema may experience feelings of frustration, embarrassment, or shame due to their condition. They may also feel isolated or misunderstood by others who do not understand the impact of eczema on their daily lives.
To address these emotional impacts, individuals with eczema may benefit from joining a support group or seeking therapy. It can also be helpful to educate friends and family about eczema and how it affects the individual’s life. Finally, taking steps to improve self-esteem and body image, such as engaging in positive self-talk or practicing self-care, can also be beneficial.
In conclusion, while eczema is primarily a physical condition, it can have significant psychological impacts as well. By understanding the relationship between stress, mental health, and eczema, individuals with eczema can take steps to address these issues and improve their overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can exposure to mold trigger eczema flare-ups?
Yes, exposure to mold can trigger eczema flare-ups. Mold spores can cause an allergic reaction in some people, leading to skin irritation and eczema flare-ups. People with eczema are more likely to have allergies, and mold is a common allergen that can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
What are the signs of eczema being aggravated by mold?
The signs of eczema being aggravated by mold are similar to the signs of eczema in general, such as redness, itching, and a rash. However, the symptoms may be more severe and persistent if mold is the trigger. If you suspect that mold is aggravating your eczema, it’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
How can mold exposure affect babies with eczema?
Babies with eczema are more susceptible to the effects of mold exposure. Mold spores can cause respiratory problems, such as wheezing and coughing, in babies with eczema. In addition, mold can exacerbate eczema symptoms, leading to more severe skin irritation and discomfort. It’s important to keep babies with eczema away from mold and other allergens as much as possible.
What are effective treatments for eczema caused by mold?
The most effective treatment for eczema caused by mold is to avoid exposure to mold as much as possible. This may involve removing mold from your home or workplace, using an air purifier, and taking other steps to reduce your exposure to mold spores. In addition, your doctor may recommend topical or oral medications to help manage your eczema symptoms.
Is there a link between atopic dermatitis and mold exposure?
Yes, there is a link between atopic dermatitis and mold exposure. Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that is often triggered by allergens, including mold. People with atopic dermatitis are more likely to have allergies, and mold is a common allergen that can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
How does contact dermatitis relate to mold allergens?
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. Mold allergens can cause contact dermatitis in some people, leading to skin irritation, redness, and itching. If you suspect that mold is causing your contact dermatitis, it’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.