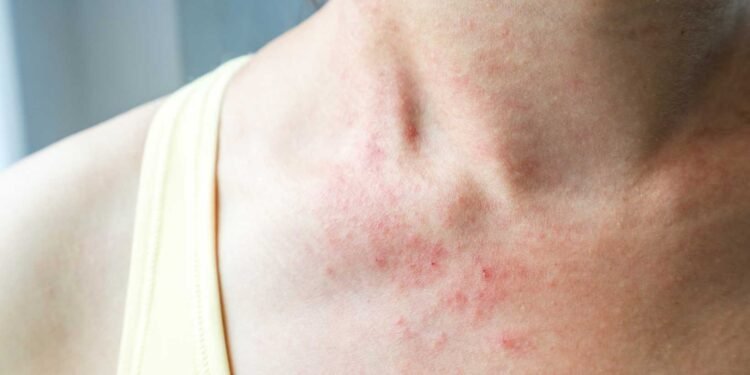
Mold is a common household allergen that can cause a variety of health problems, including skin irritation and eczema. Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While the causes of eczema are not fully understood, research has shown that mold exposure can trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms in some individuals.

Understanding the link between mold and eczema is important for those who suffer from this condition. Mold spores can irritate the skin, leading to itching, redness, and inflammation. Moreover, individuals with eczema often have a compromised skin barrier, making them more susceptible to allergens and irritants, such as mold spores. By identifying and avoiding mold exposure, individuals with eczema can reduce their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Mold exposure can trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms in some individuals.
- Mold spores can irritate the skin, leading to itching, redness, and inflammation.
- By identifying and avoiding mold exposure, individuals with eczema can reduce their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Eczema and Its Types

Defining Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is also known as atopic dermatitis, which is the most common type of eczema. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes itching, redness, and dryness of the skin. It is often accompanied by other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever.
Eczema is not contagious and is not caused by poor hygiene. It is a genetic condition that is triggered by environmental factors such as stress, allergens, and irritants. It can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in infants and young children.
Exploring the Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, and each type has its own set of symptoms and triggers. The most common types of eczema include:
-
Atopic dermatitis: This is the most common type of eczema, and it is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is often triggered by environmental factors such as allergens, stress, and irritants.
-
Contact dermatitis: This type of eczema is caused by direct contact with an irritant or allergen. It can be either allergic or irritant contact dermatitis. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the immune system reacts to an allergen, while irritant contact dermatitis occurs when the skin is exposed to an irritant.
-
Dyshidrotic eczema: This type of eczema is characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet. It is often triggered by stress or exposure to certain metals.
-
Nummular eczema: This type of eczema produces coin-shaped patches of irritated skin on the arms, legs, and torso. It is often triggered by dry skin or exposure to irritants.
In conclusion, understanding eczema and its types is crucial in managing and treating this skin condition. By identifying the type of eczema and its triggers, individuals can take steps to avoid or minimize exposure to these triggers, leading to better management of the condition.
Mold: The Unseen Allergen
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in damp and humid environments. It can grow on a variety of surfaces, including walls, ceilings, carpets, and furniture. Mold can be found both indoors and outdoors, and it can cause a range of health problems, including allergies.
Characteristics of Mold
Mold is a type of fungus that reproduces by releasing tiny spores into the air. These spores are invisible to the naked eye and can travel long distances through the air. Mold spores can survive in harsh conditions, such as extreme heat or cold, and can remain dormant for long periods of time until they find a suitable environment to grow.
Mold can come in many different colors, including black, green, white, and orange. It has a musty odor and can be easily detected by smell. Mold can grow in any area where there is moisture, including bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
Mold Spores and Allergies
Mold spores are a common allergen and can cause a range of health problems, including skin rashes and eczema. When mold spores are inhaled or come into contact with the skin, they can trigger an allergic reaction. Some of the symptoms of a mold allergy include:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Cough and postnasal drip
- Itchy eyes, nose, and throat
- Watery eyes
- Dry, scaly skin
People with eczema are particularly susceptible to mold allergies. Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. When eczema is triggered by an allergen, such as mold spores, it can cause a flare-up of symptoms.
To reduce the risk of mold allergies, it is important to keep your home dry and well-ventilated. This can be achieved by using a dehumidifier, fixing any leaks, and opening windows to allow fresh air to circulate. If you suspect that you have a mold allergy, it is important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Link Between Mold and Eczema
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in damp and humid environments. Exposure to mold can cause a variety of health problems, including respiratory issues, allergies, and skin irritation. Research has suggested that there may be a connection between mold exposure and eczema. In this section, we will explore how mold exposure affects the skin and the link between eczema and mold allergy symptoms.
How Mold Exposure Affects Skin
Mold exposure can affect the skin in several ways. When mold spores come into contact with the skin, they can cause irritation, redness, and itching. In addition, mold spores can penetrate the skin barrier and cause an allergic reaction. The skin barrier is the outermost layer of the skin that protects the body from environmental factors. When the skin barrier is compromised, it can become more susceptible to allergens and irritants, such as mold spores.
Eczema Flare-Ups and Mold Allergy Symptoms
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes red, itchy, and inflamed skin. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is believed to be related to genetics, environmental factors, and a compromised skin barrier. Research has suggested that exposure to mold can exacerbate eczema symptoms and may even trigger the development of eczema in some cases.
Mold allergy symptoms can also cause eczema flare-ups. When the body comes into contact with mold spores, it can trigger an allergic reaction. Common mold allergy symptoms include sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and skin rashes. In individuals with eczema, exposure to mold spores can cause a flare-up of eczema symptoms, such as redness, itching, and inflammation.
In conclusion, mold exposure can affect the skin and exacerbate eczema symptoms. Individuals with eczema should take steps to reduce their exposure to mold, such as keeping their homes dry and well-ventilated. If you suspect that you have a mold allergy, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the best course of treatment.
Risk Factors and Triggers

Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, several risk factors and triggers have been identified that can exacerbate eczema symptoms. In this section, we will explore some of the most common eczema triggers and risk factors.
Identifying Common Eczema Triggers
Eczema triggers can vary from person to person, but some common triggers include:
- Irritants: Exposure to irritants such as soaps, detergents, and cleaning products can trigger eczema symptoms. It is essential to identify and avoid these irritants.
- Allergens: Exposure to allergens such as pollen, pet dander, and dust mites can trigger eczema symptoms. Identifying and avoiding these allergens can help reduce eczema flare-ups.
- Stress: Stress is a common trigger for eczema. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and prevent eczema flare-ups.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes such as those that occur during pregnancy or menstruation can trigger eczema symptoms.
Environmental Factors and Mold Growth
Environmental factors such as humidity, dampness, and moisture can also trigger eczema symptoms. Mold growth is a common problem in humid and damp environments, and exposure to mold can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
Mold is a fungus that grows in damp and moist areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. Mold spores can trigger an allergic reaction in some people, leading to symptoms such as itching, redness, and inflammation. It is essential to identify and eliminate mold growth in the home to reduce the risk of eczema flare-ups.
In conclusion, identifying and avoiding eczema triggers is crucial in managing eczema symptoms. Environmental factors such as humidity, dampness, and moisture can also exacerbate eczema symptoms, and it is essential to address these factors to reduce the risk of eczema flare-ups.
Prevention and Maintenance

Mold thrives in damp and humid environments. Therefore, it is essential to take measures to reduce moisture and humidity levels in your home to prevent mold growth and minimize eczema flare-ups. Here are some tips to help you maintain a mold-free environment:
Reducing Humidity and Moisture
- Use a dehumidifier to maintain a healthy humidity level (between 30% and 50%) in your home.
- Ensure proper ventilation in damp areas, such as bathrooms and kitchens, by using exhaust fans or opening windows.
- Fix any leaks in your plumbing system, roof, or windows to prevent water accumulation and moisture buildup.
- Moisturize your skin regularly to minimize dryness and itchiness, which can trigger eczema flare-ups.
Cleaning Tips to Minimize Mold
- Regularly clean and maintain your heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system to prevent mold growth.
- Use mold-resistant paint and materials in areas prone to mold growth, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
- Clean and dry any wet or damp surfaces immediately, especially carpets, rugs, and upholstery.
- Use a mixture of vinegar and water or a commercial mold cleaner to clean moldy surfaces.
- Avoid using carpets in areas with high humidity levels, such as bathrooms and basements.
By following these prevention and maintenance tips, you can minimize mold growth in your home and reduce the risk of eczema flare-ups.
Treatment Options for Eczema and Mold Allergies
Medical Treatments and Medications
When it comes to treating eczema caused by mold allergies, there are several medical treatments and medications available. Antihistamines such as loratadine and cetirizine can help relieve itching and reduce inflammation caused by mold allergies. Topical ointments such as hydrocortisone cream can also be used to reduce inflammation and itching.
In more severe cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications such as steroids to reduce inflammation and itching. In some cases, immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be recommended to help the body build up a tolerance to mold allergens.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments and medications, there are several home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help manage eczema caused by mold allergies. One of the most important things you can do is to avoid exposure to mold as much as possible. This may mean taking steps to reduce moisture in your home, such as using a dehumidifier or fixing leaky pipes.
In terms of diet, some studies have suggested that certain foods may trigger eczema flare-ups in some people. These foods may include dairy, eggs, soy, and wheat. If you suspect that certain foods may be contributing to your eczema, it may be worth experimenting with an elimination diet to see if your symptoms improve.
Moisturizing is also an important part of managing eczema. Using a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer can help soothe dry, itchy skin and reduce the risk of flare-ups. It’s also important to avoid harsh soaps and detergents, as these can strip the skin of its natural oils and exacerbate eczema symptoms.
Overall, managing eczema caused by mold allergies can be challenging, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you are experiencing symptoms of eczema and suspect that mold exposure may be the cause, it is important to seek medical advice from a dermatologist. A dermatologist is a medical professional who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions.
Signs That You Need Professional Help
While mild cases of eczema can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments, more severe cases may require the attention of a dermatologist. Signs that you may need professional help include:
- Your eczema is causing significant discomfort or pain
- Your eczema is spreading rapidly
- You are experiencing other symptoms, such as fever or fatigue
- Your eczema is not responding to over-the-counter treatments
Getting a Diagnosis and Treatment Plan
When you visit a dermatologist, they will examine your skin and ask you questions about your symptoms and medical history. They may also perform tests to determine the cause of your eczema, such as a skin biopsy or patch test.
Once a diagnosis has been made, your dermatologist will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs. This may include prescription medications, such as topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators, as well as lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers and practicing good skin hygiene.
It is important to follow your dermatologist’s instructions closely and attend all follow-up appointments to ensure that your eczema is properly managed. With the right diagnosis and treatment plan, many people with eczema are able to effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Additional Considerations
The Role of Diet in Eczema and Allergies
While mold exposure is a known trigger for eczema, it is not the only factor that can contribute to the development of this skin condition. One important consideration is diet. Research has shown that certain foods, such as dairy, eggs, and nuts, can trigger eczema flare-ups in some people. It is important to identify and avoid these trigger foods to manage eczema.
On the other hand, there are also foods that can help alleviate eczema symptoms. Foods that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and flaxseed, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce skin inflammation. Probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and kefir, can also help improve gut health, which is linked to eczema and other health conditions.
Understanding and Managing Stress
Stress is another factor that can exacerbate eczema symptoms. When the body is under stress, it releases cortisol, a hormone that can trigger inflammation and worsen eczema. Therefore, it is important to manage stress to reduce eczema flare-ups.
There are many ways to manage stress, including exercise, meditation, and deep breathing. It is also important to get enough sleep, as lack of sleep can increase stress levels and worsen eczema symptoms. Additionally, seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can help manage stress and improve overall mental health.
Overall, while mold exposure is a known trigger for eczema, there are other factors that can contribute to the development and exacerbation of this skin condition. By understanding and managing these factors, individuals with eczema can improve their quality of life and reduce flare-ups.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of a skin rash caused by mold exposure?
Skin rashes caused by mold exposure can manifest in a variety of ways, depending on the individual’s sensitivity to mold and the type of mold present. Some common symptoms of a skin rash caused by mold exposure include itching, redness, swelling, and hives. In some cases, the rash may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as sneezing, coughing, and wheezing.
How can eczema be treated when it is related to mold exposure?
Treating eczema related to mold exposure involves addressing both the underlying cause and the symptoms of the condition. This may include identifying and removing the source of the mold, using topical or oral medications to reduce inflammation and itching, and practicing good skin hygiene. In some cases, phototherapy or other advanced treatments may be necessary to manage severe or chronic eczema.
Are infants at risk of developing eczema due to mold exposure?
Infants are particularly vulnerable to developing eczema due to mold exposure, as their immune systems are still developing and their skin is more sensitive than that of adults. Exposure to mold in infancy has been linked to an increased risk of developing eczema and other allergic conditions later in life. Parents should take steps to minimize their child’s exposure to mold, such as keeping their living spaces clean and dry and avoiding areas with visible mold growth.
Can exposure to mold trigger a flare-up of eczema symptoms?
Yes, exposure to mold can trigger a flare-up of eczema symptoms in individuals who are sensitive to mold. This is because mold spores can irritate the skin and cause inflammation, leading to itching, redness, and other symptoms of eczema. People with eczema should take steps to minimize their exposure to mold, such as keeping their living spaces clean and dry and avoiding areas with visible mold growth.
What are common indicators of mold toxicity that one should be aware of?
Common indicators of mold toxicity include respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath; neurological symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and memory loss; and skin symptoms such as rashes, itching, and hives. Other symptoms may include fatigue, muscle weakness, and digestive problems. If you suspect that you may be experiencing mold toxicity, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
How can one definitively diagnose a skin condition caused by mold?
Definitively diagnosing a skin condition caused by mold requires a thorough medical evaluation, including a physical exam, medical history, and diagnostic testing. This may include skin patch testing, blood tests, and other specialized tests to identify the specific type of mold present and determine the best course of treatment. It is important to work closely with a qualified healthcare provider to ensure an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.