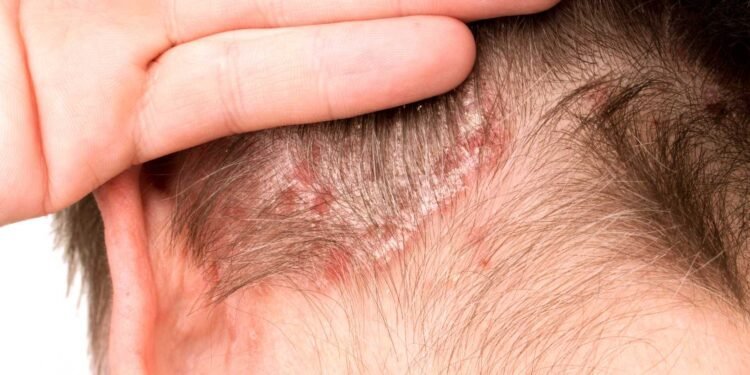
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing it to become red, itchy, and scaly. It is a condition that can be triggered by various factors, including stress, infections, and injuries. However, there is growing evidence that suggests that mold exposure may also be a contributing factor to psoriasis symptoms. Mold is a type of fungus that can grow in damp and humid environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. When mold spores are inhaled or come into contact with the skin, they can cause allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and skin irritation.

Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes the skin cells to grow too quickly, resulting in red, scaly patches on the skin. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Psoriasis can be triggered by stress, infections, injuries, and certain medications.
Mold is a type of fungus that can grow in damp and humid environments. When mold spores are inhaled or come into contact with the skin, they can cause allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and skin irritation. Mold exposure can also aggravate existing skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis. Mold can release mycotoxins, which can cause a range of health problems, including skin rashes, headaches, and fatigue.
Key Takeaways
- Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing it to become red, itchy, and scaly.
- Mold exposure may be a contributing factor to psoriasis symptoms, as mold can aggravate existing skin conditions and cause skin irritation.
- Preventive measures, such as reducing mold exposure, can help manage psoriasis symptoms.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by an overactive immune system that mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to the buildup of skin cells on the surface of the skin. This results in red, scaly, and often itchy patches on different parts of the body.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a non-contagious skin condition that affects people of all ages and genders. It is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, it is thought to be triggered by an immune system malfunction that causes skin cells to grow too quickly.
Common Symptoms and Signs
The most common symptoms of psoriasis include dry, cracked skin that may bleed, itching, burning or soreness, and cyclic rashes that flare for a few weeks or months and then subside. The severity of these symptoms can vary from person to person and can be influenced by factors such as stress, diet, and lifestyle.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each of which varies in its signs and symptoms. The most common type of psoriasis is plaque psoriasis, which causes dry, itchy, raised skin patches (plaques) covered in silver scales. Another type of psoriasis is guttate psoriasis, which is characterized by small, drop-shaped lesions that appear on the arms, legs, trunk, and scalp. Psoriatic arthritis is a type of psoriasis that affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of psoriasis is crucial to identifying and managing its symptoms. While psoriasis is a chronic condition, it can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes.
Mold Exposure and Its Effects

The Role of Mold in Indoor Environments
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in damp and humid environments. It can be found both indoors and outdoors. In indoor environments, mold can grow on walls, ceilings, floors, carpets, and other surfaces. It can also grow in air conditioning systems, humidifiers, and other appliances that produce moisture. Mold spores can spread through the air and can be inhaled by people.
Health Implications of Mold Exposure
Exposure to mold can have various health implications. Some people are more sensitive to mold than others. For people with psoriasis, exposure to mold can trigger or worsen their symptoms. Mold exposure can also cause respiratory problems, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. It can also cause allergic reactions, such as sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes. In some cases, mold exposure can lead to fungal infections, which can be serious for people with weakened immune systems.
When mold is present in indoor environments, it is important to take steps to prevent its growth. This includes keeping indoor environments dry and well-ventilated, fixing leaks and water damage promptly, and using air purifiers and dehumidifiers as needed. If mold is present, it should be removed promptly and properly to prevent further growth and exposure. In some cases, professional mold remediation may be necessary.
In summary, mold exposure can have various health implications, including triggering or worsening psoriasis symptoms. It is important to take steps to prevent mold growth and to remove mold promptly if it is present.
Link Between Psoriasis and Mold
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the skin, causing it to become inflamed, red, and scaly. While the exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, research suggests that environmental factors can trigger or worsen the condition. One such factor is mold.
Can Mold Trigger Psoriasis?
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in warm, damp environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. Exposure to mold can cause a range of health problems, including allergies, respiratory issues, and skin irritation. In some cases, mold exposure can also trigger psoriasis or make existing symptoms worse.
According to a resource on mypsoriasisteam.com, mold isn’t necessarily the sole cause of psoriasis, but individuals could be sensitive to it. Doctors can check for various common allergies, including mold, to help identify potential triggers that are making psoriasis symptoms worse. If an individual is allergic to mold, they may be advised to take over-the-counter or prescription allergy medications to reduce inflammation or avoid exposure to mold altogether.
Aggravation of Psoriasis Symptoms by Mold
Mold exposure can also aggravate existing psoriasis symptoms. In a review article published on ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, the authors suggest that psoriasis can be induced or aggravated by various environmental factors, including infection, alcohol consumption, drugs, trauma, acute withdrawal of systemic or potent topical corticosteroids, and exposure to mold.
In addition, clevelandclinic.org reports that psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, scaly patches, or plaques. Although it’s not contagious, its symptoms tend to ebb and flow like other chronic inflammatory diseases. Psoriasis flare-ups can be triggered or worsened by a range of environmental factors, including stress, infections, and exposure to mold.
In conclusion, while mold may not be the sole cause of psoriasis, it can trigger or worsen symptoms in some individuals. It is essential to identify potential triggers and avoid exposure to them to manage psoriasis symptoms effectively.
Identifying Psoriasis Triggers

Psoriasis is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no known cure for psoriasis, identifying triggers that cause flare-ups can help manage the condition. This section will discuss common triggers for psoriasis and environmental factors that may aggravate the condition.
Common Triggers for Psoriasis
Psoriasis triggers can vary from person to person. However, some common triggers include stress, injury to the skin, infections, and certain medications. Stress is a common trigger for psoriasis, and it can worsen existing symptoms. Injuries to the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, or burns, can also trigger psoriasis. Certain medications, such as beta-blockers and lithium, can also cause flare-ups.
Environmental Factors and Psoriasis
Environmental factors can also play a role in triggering or aggravating psoriasis. Weather changes, such as cold and dry weather, can dry out the skin and increase the chances of a flare-up. On the other hand, hot and sunny weather appears to help relieve symptoms for some people. Smoking and alcohol consumption have also been linked to psoriasis, and quitting these habits can help manage symptoms. Obesity is another factor that can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
One environmental factor that has gained attention recently is mold. While there is limited research on the link between mold and psoriasis, some studies suggest that mold exposure can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms. Environmental mold can be indoor or outdoor, and it’s a good idea to have an allergy test if you suspect mold as a trigger.
Identifying psoriasis triggers can be a process of trial and error. Keeping a journal of symptoms and triggers can help identify patterns and manage the condition. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that includes identifying and managing triggers.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Diagnosing Psoriasis
Diagnosing psoriasis involves a physical examination, medical history review, and laboratory tests. A dermatologist will typically perform a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. The biopsy involves taking a small sample of skin tissue, which is then examined under a microscope to determine if it contains the characteristic features of psoriasis.
In addition to the biopsy, a dermatologist may also order blood tests to rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms. These tests may include a complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests, and a test for rheumatoid factor.
Treating Psoriasis Effectively
There is currently no cure for psoriasis, but there are a variety of treatments available to help manage the symptoms. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition and may include topical creams, light therapy, oral medications, and biologics.
Topical creams, such as corticosteroids, are often the first line of treatment for mild to moderate psoriasis. These creams work by reducing inflammation and slowing down the growth of skin cells. Light therapy, or phototherapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light, which can also help to slow down the growth of skin cells.
For more severe cases of psoriasis, oral medications may be necessary. These medications include retinoids, methotrexate, and cyclosporine. Biologics, which are a newer class of medications, work by targeting specific parts of the immune system that are involved in the development of psoriasis.
Overall, the most effective treatment plan for psoriasis will depend on the individual and their specific symptoms. It is important to work closely with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the unique needs of each patient.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, smoking, obesity, diet, and alcohol consumption. However, some people may find that their psoriasis symptoms are aggravated by mold exposure. In this section, we will discuss some preventive measures and lifestyle changes that can help manage psoriasis triggers and improve outcomes.
Managing Psoriasis Triggers
One of the most important steps in managing psoriasis is identifying and avoiding triggers. Some common triggers include stress, infections, and certain medications. In addition, mold exposure can also trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms. To reduce the risk of mold exposure, it is important to keep your home clean and dry, fix any leaks or water damage promptly, and use a dehumidifier in damp areas. You may also want to consider having your home tested for mold if you suspect that it may be a problem.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Outcomes
In addition to avoiding triggers, there are several lifestyle adjustments that can help improve psoriasis outcomes. For example, maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Smoking cessation is also important, as smoking can worsen psoriasis symptoms and increase the risk of other health problems.
Alcohol consumption should also be limited, as excessive drinking can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms. Some studies have also suggested that a gluten-free diet may be beneficial for some people with psoriasis, although more research is needed to confirm this. Finally, reducing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can also help manage psoriasis symptoms.
In summary, managing psoriasis triggers and making lifestyle adjustments can help improve outcomes for people with psoriasis. By avoiding triggers such as mold exposure, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and reducing stress, people with psoriasis can reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Potential Complications of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin and joints. While it is primarily known for causing red, scaly patches on the skin, it can also lead to a range of complications that affect other parts of the body.
Psoriatic Arthritis and Joint Issues
One of the most common complications of psoriasis is psoriatic arthritis, which affects up to 30% of people with psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. It can affect any joint in the body, but is most commonly found in the fingers, toes, and spine.
In addition to psoriatic arthritis, people with psoriasis may also experience other joint issues, such as tendinitis and carpal tunnel syndrome. These conditions can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
Comorbidities Associated with Psoriasis
Psoriasis is also associated with a number of comorbidities, or other conditions that occur alongside it. These comorbidities can be caused by the chronic inflammation that psoriasis triggers in the body.
One common comorbidity is depression. People with psoriasis are more likely to experience depression than those without the condition. This may be due to the physical and emotional toll that psoriasis takes on the body.
Other comorbidities associated with psoriasis include cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and liver disease. These conditions are all linked to inflammation, which is a hallmark of psoriasis.
Overall, it is important for people with psoriasis to be aware of the potential complications associated with the condition. By working closely with a healthcare provider, they can manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of developing comorbidities.
Support and Resources
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but finding the right support and resources can make a big difference in managing the condition. Here are some resources that can help:
Finding Support for Psoriasis
Having a support system can be crucial for people with psoriasis. Support can come from many sources, including family, friends, healthcare providers, and support groups. The National Psoriasis Foundation is a great place to start looking for support. They offer a variety of resources, including a community forum where people with psoriasis can connect with others who understand what they’re going through. The foundation also provides information on local support groups, which can be a great way to meet others in person.
Educational Resources and Communities
There are many educational resources available for people with psoriasis. The National Psoriasis Foundation offers a wealth of information on their website, including articles on managing psoriasis, treatment options, and the latest research. They also provide a free magazine, Psoriasis Advance, which is full of helpful tips and stories from people with psoriasis.
In addition to the National Psoriasis Foundation, there are many online communities where people with psoriasis can connect and share information. Some popular communities include MyPsoriasisTeam, Inspire, and PatientsLikeMe. These communities can be a great source of support and information, as well as a place to connect with others who are going through similar experiences.
It’s important to remember that psoriasis can have a genetic component, so it’s possible that other family members may also be affected. If you have a family history of psoriasis, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor about your risk and any steps you can take to manage the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of mold biotoxin illness that overlap with psoriasis?
Mold biotoxin illness symptoms can include fatigue, brain fog, muscle aches, joint pain, and sensitivity to light and sound. These symptoms may overlap with psoriasis symptoms, such as fatigue, joint pain, and sensitivity to light. However, mold biotoxin illness symptoms can also include respiratory issues, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, which are not typically associated with psoriasis.
How can one test for biotoxin illness due to mold exposure?
There are several tests available to diagnose biotoxin illness due to mold exposure. These tests include blood tests, urine tests, and visual contrast sensitivity tests. It is important to note that some of these tests may not be covered by insurance and can be expensive.
Can mold exposure be a significant trigger for psoriasis flare-ups?
While mold exposure is not a direct cause of psoriasis, it can be a trigger for psoriasis flare-ups in some individuals. Mold exposure can cause inflammation, which can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. If an individual suspects that mold exposure is triggering their psoriasis flare-ups, they should consult with their healthcare provider.
What treatments are available for biotoxin illness that may also benefit psoriasis symptoms?
Treatment for biotoxin illness due to mold exposure typically involves addressing the mold exposure and detoxifying the body. This may include removing the source of mold, using air filters, and taking binders to remove toxins from the body. These treatments may also benefit psoriasis symptoms by reducing inflammation in the body.
Are there any specific signs that indicate a psoriasis infection might be exacerbated by mold toxins?
There are no specific signs that indicate a psoriasis infection might be exacerbated by mold toxins. However, if an individual with psoriasis experiences worsening symptoms after exposure to mold, it may be an indication that mold is exacerbating their psoriasis symptoms.
What are the early warning signs of mold toxicity that individuals with psoriasis should be aware of?
Early warning signs of mold toxicity can include fatigue, brain fog, muscle aches, joint pain, and sensitivity to light and sound. These symptoms may overlap with psoriasis symptoms, so it is important for individuals with psoriasis to be aware of their exposure to mold and to consult with their healthcare provider if they experience worsening symptoms after exposure to mold.