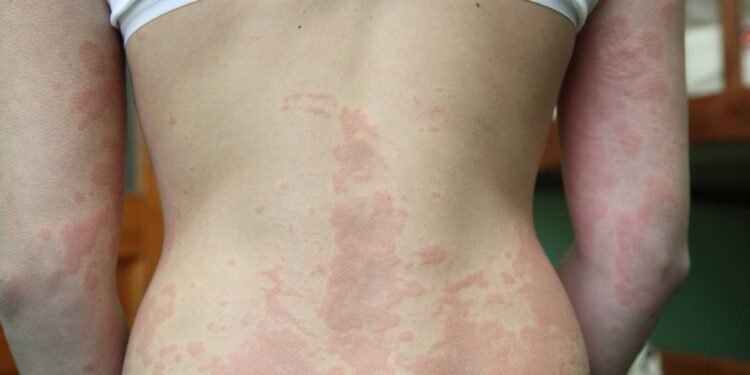
Exposure to mold can cause a range of health problems, including respiratory issues, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. In some cases, it can even exacerbate pre-existing conditions like dermatitis. Dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes redness, itching, and inflammation. While it can be caused by a variety of factors, mold exposure is one potential trigger that should not be overlooked.

Understanding Dermatitis and Mold Exposure
Dermatitis is a skin condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and exposure to irritants. Mold exposure is one potential cause of dermatitis. Mold can grow in damp, humid areas, and can be found in homes, schools, and other buildings. When mold spores are inhaled or come into contact with the skin, they can cause a range of symptoms, including skin irritation, itching, and redness.
Symptoms of Mold-Related Dermatitis
The symptoms of mold-related dermatitis can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include redness, itching, and inflammation of the skin. In some cases, blisters may also form. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms and suspect that mold may be the cause, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Dermatitis can be caused or exacerbated by exposure to mold.
- Symptoms of mold-related dermatitis can include redness, itching, and inflammation of the skin.
- If you suspect that mold may be causing your dermatitis symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause.
Understanding Dermatitis and Mold Exposure
The Basics of Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a skin condition that causes inflammation and irritation of the skin. It can cause redness, itching, and sometimes blistering. There are several types of dermatitis, including contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis is caused by exposure to an irritant or allergen, and can occur anywhere on the body. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that causes itchy, scaly patches on the skin, and usually develops in childhood. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common condition that causes scaly patches, red skin, and dandruff.
Role of Mold in Dermatitis
Mold is a type of fungus that can grow in damp environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. Mold spores can trigger allergic reactions in some people, causing symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, and itchy eyes.
In addition to causing respiratory symptoms, mold exposure can also exacerbate dermatitis symptoms. According to a Healthline article, mold can cause skin rashes and other dermatitis symptoms. Mold spores can also irritate the skin, causing redness and itching.
People with weakened immune systems or pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema, are more susceptible to mold-related dermatitis. It is important to identify and treat mold growth in the home to prevent exposure and reduce the risk of dermatitis symptoms.
In summary, mold exposure can exacerbate dermatitis symptoms and cause skin rashes. It is important to identify and treat mold growth in the home to prevent exposure and reduce the risk of dermatitis symptoms.
Symptoms of Mold-Related Dermatitis
Mold can cause or aggravate dermatitis symptoms. Dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, and itchiness. Mold-related dermatitis can be caused by direct contact with mold or by inhaling mold spores. In this section, we will discuss the common symptoms of mold-related dermatitis.
Identifying Common Symptoms
Mold-related dermatitis can manifest in different ways depending on the individual’s sensitivity to mold and the type of mold they are exposed to. The most common symptoms of mold-related dermatitis include:
-
Rash: A rash is a common symptom of mold-related dermatitis. The rash can be red, itchy, and swollen. It can appear on any part of the body that has come into contact with mold.
-
Itchy skin: Itchy skin is another common symptom of mold-related dermatitis. The skin may feel dry and scaly, and scratching can lead to further inflammation.
-
Inflammation: Inflammation is a hallmark symptom of dermatitis. Inflammation can cause the skin to become red, swollen, and painful.
Distinguishing Mold Allergy Symptoms
Mold allergy symptoms can be similar to dermatitis symptoms, but there are some key differences. If an individual is allergic to mold, they may experience the following symptoms:
-
Sneezing: Sneezing is a common symptom of mold allergies. Sneezing can be accompanied by a runny or stuffy nose.
-
Itchy eyes: Itchy, watery eyes are a common symptom of mold allergies. Eye irritation can be accompanied by redness and swelling.
-
Coughing: Coughing is a common symptom of mold allergies. Coughing can be accompanied by wheezing and shortness of breath.
It is important to note that not all individuals who are exposed to mold will develop dermatitis or mold allergies. However, if an individual experiences any of the symptoms mentioned above after being exposed to mold, they should seek medical attention.
Factors Contributing to Mold Growth

Mold growth is a common problem in many households, and it can cause various health issues, including dermatitis. Understanding the factors that contribute to mold growth is essential in preventing and managing mold-related health problems.
Damp Environments and Moisture
Mold thrives in damp environments and requires moisture to grow. Therefore, areas with high humidity levels, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements, are more prone to mold growth. Leaks or water damage can also create damp environments that promote mold growth.
To prevent mold growth, it is essential to keep the indoor environment dry. Regularly check for leaks or water damage and repair them promptly. Proper ventilation and dehumidification can also help reduce indoor moisture levels and prevent mold growth.
Poor Ventilation and Mold Proliferation
Poor ventilation can contribute to mold proliferation, especially in areas with high humidity levels. Without proper ventilation, moisture can accumulate, creating a conducive environment for mold growth.
To prevent mold growth, ensure proper ventilation in your home. Use exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens to reduce moisture levels. Open windows and doors to increase air circulation and reduce indoor humidity levels.
It is important to note that not all mold is toxic, and not all toxic molds are black. However, some molds, such as black mold, can produce toxic spores that can cause health problems, including dermatitis. Therefore, it is essential to prevent mold growth and address mold problems promptly to avoid health issues.
Diagnosis and Testing for Mold Allergies
Mold allergy can cause a variety of symptoms, including skin rashes, coughing, sneezing, and shortness of breath. If you suspect that you have a mold allergy, you should see a doctor for a professional assessment.
Professional Assessment by a Doctor
During your appointment, the doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. They may also perform a physical examination to check for signs of an allergic reaction, such as skin rashes or hives. Based on your symptoms and medical history, the doctor may recommend allergy testing to determine whether you are allergic to mold.
Allergy Testing Methods
There are two main types of allergy testing: blood tests and skin prick tests. Blood tests measure the amount of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in your blood. IgE antibodies are produced by your immune system in response to allergens like mold. A high level of IgE antibodies in your blood can indicate that you are allergic to mold.
Skin prick tests involve placing a small amount of mold extract on your skin and then pricking the skin with a needle. If you are allergic to mold, your skin will become red and swollen at the site of the prick.
Both blood tests and skin prick tests are effective for diagnosing mold allergies. Your doctor will recommend the best testing method based on your symptoms and medical history.
It is important to note that a positive allergy test does not necessarily mean that you will experience symptoms when exposed to mold. Your doctor will use the results of your allergy test, along with your symptoms and medical history, to make a diagnosis and recommend treatment options.
Treatment Options for Mold-Induced Dermatitis

If someone is experiencing dermatitis symptoms due to mold exposure, it is important to seek treatment to alleviate the discomfort. Treatment options for mold-induced dermatitis can be divided into two categories: medical treatments and home remedies.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments for mold-induced dermatitis may include the following:
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines are a common medication used to treat allergic reactions, including dermatitis caused by mold exposure. They work by blocking the histamine receptors in the body, which reduces itching, swelling, and other allergy symptoms.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are another medication that may be prescribed to treat dermatitis caused by mold exposure. They work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system’s response to the allergen.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a treatment that involves exposing the body to small amounts of the allergen over time to build up a tolerance. This treatment can be effective for people with severe allergies who do not respond to other treatments.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, there are also several home remedies and lifestyle changes that can be made to alleviate symptoms of mold-induced dermatitis. These include:
- Reducing exposure to mold: The best way to prevent dermatitis caused by mold exposure is to reduce exposure to mold. This can be done by cleaning and drying areas that are prone to mold growth, using a dehumidifier, and fixing any leaks or water damage in the home.
- Moisturizing: Moisturizing the affected area can help alleviate itching and dryness associated with dermatitis. It is important to use a fragrance-free moisturizer to avoid further irritation.
- Using over-the-counter creams and ointments: Over-the-counter creams and ointments, such as hydrocortisone cream, can help alleviate itching and inflammation associated with dermatitis.
- Avoiding irritants: People with dermatitis caused by mold exposure should avoid using harsh soaps, detergents, and other irritants that can exacerbate symptoms.
It is important to note that while home remedies can provide relief, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical attention.
Preventing Mold Exposure and Dermatitis

Dermatitis symptoms can be caused or aggravated by mold exposure. Therefore, it is important to take measures to prevent mold growth in the environment. The following subsections provide information on environmental control and mold remediation techniques.
Environmental Control
To prevent mold growth and exposure, it is important to control the environment. The following measures can be taken:
- Keep humidity levels low: Mold thrives in humid environments, so it is important to keep indoor humidity levels below 60%.
- Use a dehumidifier: A dehumidifier can help reduce humidity levels in the environment.
- Increase ventilation: Proper ventilation can help prevent moisture buildup and reduce the risk of mold growth.
- Fix leaks: Leaks in pipes, roofs, and windows should be fixed promptly to prevent moisture buildup.
- Showering: After showering, it is important to keep the bathroom well-ventilated and dry to prevent moisture buildup.
Mold Remediation Techniques
If mold growth is already present, remediation techniques can be used to remove it and prevent further exposure. The following techniques can be used:
- Clean and dry surfaces: Mold can be removed from hard surfaces using soap and water, and then dried thoroughly.
- Use mold-killing products: Products such as bleach, hydrogen peroxide, and vinegar can be used to kill mold on hard surfaces.
- Remove and replace porous materials: Porous materials such as carpet, drywall, and ceiling tiles may need to be removed and replaced if mold growth is present.
- Hire a professional: If mold growth is extensive, it may be necessary to hire a professional mold remediation company to remove it safely and effectively.
By taking these measures, individuals can prevent mold exposure and reduce the risk of dermatitis symptoms caused or aggravated by mold.
Complications and Health Risks of Mold
Mold exposure can lead to a variety of health complications, especially for individuals with compromised immune systems, asthma, or other respiratory conditions. The severity of the symptoms can depend on the type of mold and the length and extent of exposure.
Respiratory Issues and Asthma
Mold can lead to respiratory issues, including coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. For individuals with asthma, mold can trigger asthma attacks and exacerbate symptoms. According to a study by the Institute of Medicine, exposure to mold can cause new-onset asthma in some individuals.
Long-Term Health Implications
Long-term exposure to mold can lead to more serious health complications, including hypersensitivity pneumonitis and other chronic respiratory conditions. In rare cases, mold exposure has been linked to the development of certain cancers.
It is important to address mold growth in the home or workplace to prevent potential health risks. Individuals with compromised immune systems or respiratory conditions should take extra precautions to avoid exposure to mold. If mold is suspected, it is recommended to consult a professional for proper remediation and removal.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
Dermatitis can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition to live with. While mild cases can often be managed with over-the-counter remedies, more severe or persistent symptoms may require professional medical attention. Here are some signs that it may be time to seek the advice of a healthcare provider:
Recognizing Severe Allergic Reactions
In some cases, dermatitis symptoms may be caused or aggravated by an allergic reaction to mold. Severe allergic reactions can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Rapid or weak pulse
- Dizziness or fainting
- Severe itching or hives
If you experience any of these symptoms, call 911 or seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
If your dermatitis symptoms are persistent, severe, or impacting your quality of life, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider. They can help you determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Some factors that may increase your risk of developing severe dermatitis symptoms include:
- A compromised immune system
- Asthma or other respiratory conditions
- Exposure to high levels of mold or other environmental irritants
Your healthcare provider may recommend a variety of treatments, including:
- Topical creams or ointments
- Oral medications
- Allergy shots
- Lifestyle changes to reduce exposure to environmental irritants
In some cases, your healthcare provider may refer you to a specialist, such as an allergist or dermatologist, for further evaluation and treatment.
Overall, if you are experiencing persistent or severe dermatitis symptoms, it is important to seek professional medical advice. With the right treatment plan, you can manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs of a skin rash caused by mold exposure?
Skin rash caused by mold exposure can manifest itself in different ways. Common signs of a skin rash caused by mold exposure include redness, itching, and swelling. The affected area may also become dry, scaly, or develop a rash. In some cases, dermatitis can cause a burning or stinging sensation.
How can I distinguish between dermatitis and a mold-induced skin reaction?
Dermatitis can be caused by many factors, including mold exposure. However, it is difficult to distinguish between dermatitis and a mold-induced skin reaction since the symptoms are similar. If you suspect that your skin rash is due to mold exposure, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause of your symptoms.
What symptoms indicate an indoor mold allergy might be affecting my skin?
If you have an indoor mold allergy, you may experience symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. In some cases, mold exposure can also cause skin irritation, rashes, and hives. If you suspect that your skin symptoms are due to mold exposure, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause of your symptoms.
Can exposure to mold spores directly cause skin irritation or hives?
Yes, exposure to mold spores can directly cause skin irritation or hives. Mold spores can cause an allergic reaction, which can lead to skin symptoms such as itching, redness, and hives.
Is there a link between mold in the home and eczema flare-ups in infants?
There is evidence to suggest that exposure to mold in the home may trigger eczema flare-ups in infants. If you suspect that mold exposure is causing your child’s eczema symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause of your child’s symptoms.
What unusual symptoms might suggest a skin infection is due to mold toxicity?
Unusual symptoms that might suggest a skin infection is due to mold toxicity include fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. If you experience these symptoms along with skin irritation or rash, it is important to seek medical attention right away.