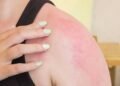
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection that commonly affects the feet. It is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm and moist environments. Athlete’s foot can be uncomfortable and even painful, with symptoms ranging from itching, burning, and stinging to blisters and peeling skin. While the condition is generally not serious, it can be persistent and may lead to complications if left untreated.

Mold exposure is another common problem that can cause a range of health issues. Mold is a type of fungus that grows in damp and humid environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. Mold can cause allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and other health issues. There is some evidence to suggest that mold exposure may also be linked to athlete’s foot, either by causing the condition or aggravating its symptoms.
Understanding Athlete’s Foot and Mold Exposure
Causes of Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. The fungus responsible for athlete’s foot thrives in warm and moist environments, such as locker rooms, public showers, and swimming pools. The infection is highly contagious and can be easily spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects. People who frequently wear tight-fitting shoes or socks, or who have sweaty feet, are at a higher risk of developing athlete’s foot.
The Role of Mold in Skin Infections
Mold exposure has been linked to a variety of health problems, including skin infections like athlete’s foot. Mold spores are present in the air we breathe, and they can settle on surfaces and multiply in warm and moist environments. When mold spores come into contact with the skin, they can cause irritation and inflammation, which can lead to the development of a skin infection.
While mold exposure can aggravate athlete’s foot symptoms, it is not the primary cause of the infection. Athlete’s foot is caused by a type of fungus called dermatophyte, which can be found in soil, animals, and humans. Mold exposure can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections, including athlete’s foot.
To prevent athlete’s foot and other skin infections, it is important to maintain good hygiene practices, such as washing your feet regularly with soap and water, and keeping them dry. Wearing breathable shoes and socks, and avoiding walking barefoot in public areas can also help reduce the risk of developing athlete’s foot. If you suspect that you have athlete’s foot, it is important to seek medical treatment to prevent the infection from spreading and to alleviate symptoms.
In summary, while mold exposure can aggravate athlete’s foot symptoms, it is not the primary cause of the infection. Athlete’s foot is caused by a type of fungus, and can be easily prevented by maintaining good hygiene practices and avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces.
Identifying Symptoms and Diagnosis

Common Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot is a common fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. The symptoms of athlete’s foot can vary from person to person, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Itchy, red, and scaly skin between the toes
- Blisters on the feet that itch
- Burning or stinging sensation on the feet
- Cracking and peeling skin on the feet, especially between the toes
Athlete’s foot can also cause a rash on the feet that may spread to other parts of the body. In severe cases, the skin may become thick and discolored, and blisters may develop that ooze or become crusty.
Diagnosing Fungal and Mold-Related Skin Conditions
To diagnose athlete’s foot or other fungal and mold-related skin conditions, a doctor or dermatologist will typically examine the affected area and ask about the patient’s symptoms. In some cases, the doctor may take a skin sample to examine under a microscope or send it to a lab for testing.
Other tests that may be used to diagnose athlete’s foot include a skin culture, which involves taking a sample of the affected skin and growing it in a lab to identify the type of fungus or mold that is causing the infection. Blood tests may also be used to check for signs of infection or to rule out other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have athlete’s foot or another fungal or mold-related skin condition. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the infection from spreading and reduce the risk of complications.
Preventive Measures Against Fungal Infections

Fungal infections such as athlete’s foot can be prevented by taking some simple steps. Here are some preventive measures that can help reduce the risk of fungal infections:
Reducing Moisture and Promoting Dry Feet
Moisture is a breeding ground for fungi, so keeping your feet dry is essential in preventing fungal infections. Here are some tips to reduce moisture and promote dry feet:
- Dry your feet thoroughly after bathing, swimming, or exercise.
- Wear moisture-wicking socks that can help keep your feet dry.
- Use foot powder to absorb moisture and reduce friction.
- Avoid wearing tight shoes that can trap moisture.
Proper Footwear and Hygiene Practices
Wearing the right footwear and practicing good hygiene can also help prevent fungal infections. Here are some tips:
- Wear shoes or sandals in public areas, such as locker rooms and swimming pools.
- Avoid sharing shoes or socks with others.
- Wash your feet daily with soap and water.
- Keep your toenails trimmed and clean.
- Change your socks and shoes regularly to keep your feet clean and dry.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of developing fungal infections such as athlete’s foot.
Treatment Options for Athlete’s Foot

Over-the-Counter Treatments
When it comes to managing Athlete’s Foot, individuals can opt for over-the-counter antifungal creams that contain active ingredients such as clotrimazole, terbinafine, or miconazole. These creams are easily accessible and can effectively alleviate the symptoms of Athlete’s Foot, including itching, redness, and scaling. It is essential to carefully follow the instructions provided with the product and continue using the cream for the recommended duration to ensure the infection is fully treated.
Prescription Medications and Topical Creams
In cases where over-the-counter treatments may not provide sufficient relief, prescription antifungal medications and topical creams may be necessary. These stronger formulations are often recommended for severe or persistent cases of Athlete’s Foot. Physicians may prescribe oral antifungal medications or stronger topical creams to combat the infection more effectively. It is crucial for individuals to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable prescription-based treatment based on the severity of their condition.
Environmental Factors and Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection of the skin on the feet that can cause itchiness, burning, and cracking. While the condition is typically caused by a fungus that thrives in warm, moist environments, other environmental factors may also play a role in the development and exacerbation of athlete’s foot symptoms.
Exposure to Mold in Public Places
Mold is a common environmental factor that can contribute to the development of athlete’s foot symptoms. Mold thrives in warm, damp environments, such as public showers, swimming pools, and locker rooms. When individuals come into contact with mold in these public areas, they may be at an increased risk of developing athlete’s foot.
To reduce the risk of exposure to mold in public places, individuals should wear protective footwear, such as flip-flops or sandals, when using public showers, pools, or locker rooms. It is also important to dry feet thoroughly after showering or swimming to prevent the growth of mold and other fungi.
Risk Factors in Communal Settings
In addition to exposure to mold, there are several other risk factors for athlete’s foot in communal settings. These include:
- Walking barefoot in public areas
- Sharing towels, socks, or shoes with others
- Using communal nail clippers or other grooming tools
To reduce the risk of developing athlete’s foot in communal settings, individuals should avoid walking barefoot in public areas and should not share towels, socks, or shoes with others. It is also important to keep feet clean and dry, and to avoid using communal grooming tools whenever possible.
Overall, while environmental factors such as mold and communal settings can contribute to the development of athlete’s foot symptoms, there are several steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of infection. By taking these precautions, individuals can help prevent the development and spread of athlete’s foot, and can enjoy healthy, comfortable feet.
Complications and Coexisting Conditions
Athlete’s foot is a fungal skin infection that can lead to complications and coexisting conditions if left untreated. Some of the common complications of athlete’s foot include bacterial infections, which can lead to swelling, redness, and pain in the affected area. In severe cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, causing fever and chills.
When Athlete’s Foot Leads to Secondary Infections
When athlete’s foot is left untreated, it can lead to secondary bacterial infections. This is because the fungus that causes athlete’s foot can weaken the skin’s natural defenses, making it more susceptible to bacterial infections. In some cases, the bacterial infection can be severe and require medical attention. People with diabetes, poor circulation, or a weakened immune system are at a higher risk of developing secondary infections.
The Impact of Athlete’s Foot on Overall Health
Athlete’s foot can also have an impact on a person’s overall health. The constant itching and burning sensation can cause discomfort and disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and irritability. In addition, people with athlete’s foot may feel self-conscious about their condition, which can affect their mental health and quality of life.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have athlete’s foot or if your symptoms do not improve with treatment. This is especially true if you have diabetes or a weakened immune system, as these conditions can increase your risk of complications. With proper treatment and good foot hygiene, most cases of athlete’s foot can be successfully treated without any long-term complications.
When to See a Healthcare Professional
If you have athlete’s foot symptoms and suspect that mold may be the cause or aggravating factor, there are certain signs that indicate you need to seek medical attention. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help you get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Signs That You Need Medical Attention
If you have athlete’s foot symptoms that are not responding to over-the-counter treatments, it may be time to see a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you have a compromised immune system, diabetes, or other underlying health conditions, it is important to see a healthcare professional as soon as possible. These conditions can increase your risk of developing complications from athlete’s foot.
Other signs that you need medical attention include:
- Severe pain or discomfort
- Swelling or redness that spreads beyond the foot
- Blisters that become infected
- Fever or chills
- Numbness or tingling in the affected area
Consulting with a Dermatologist
A dermatologist is a healthcare professional who specializes in diagnosing and treating skin conditions. If you suspect that mold may be the cause or aggravating factor of your athlete’s foot symptoms, a dermatologist can help you get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
During your appointment, the dermatologist will examine your feet and ask about your symptoms. They may also take a sample of the affected skin to test for mold or other fungi. Based on your diagnosis, the dermatologist may recommend antifungal medications, topical creams, or other treatments.
It is important to follow the dermatologist’s treatment plan and take all medications as prescribed. If you have any questions or concerns about your treatment, be sure to speak with your healthcare professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
What environmental factors contribute to the development of athlete’s foot?
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection that thrives in warm, moist environments such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and public showers. Walking barefoot in these areas can increase the risk of contracting the infection. Additionally, wearing tight-fitting shoes or socks that do not allow proper ventilation can also contribute to the development of athlete’s foot.
How can certain types of fungi, including mold, exacerbate athlete’s foot symptoms?
While mold itself does not cause athlete’s foot, it can worsen the symptoms of an existing infection. This is because mold spores can irritate the skin and cause inflammation, which can lead to itching, burning, and peeling. In some cases, exposure to mold can also trigger an allergic reaction, which can further exacerbate athlete’s foot symptoms.
What are the common triggers that cause athlete’s foot to worsen?
Athlete’s foot can worsen when the infected area is exposed to moisture, such as sweating or walking barefoot in damp areas. Wearing tight-fitting shoes or socks can also exacerbate symptoms. Additionally, certain activities such as swimming or showering can contribute to the development of athlete’s foot.
Why are some individuals more susceptible to recurring athlete’s foot infections?
Some individuals may be more susceptible to recurring athlete’s foot infections due to a weakened immune system or underlying health conditions such as diabetes. Additionally, those who frequently engage in activities that involve exposure to warm, moist environments may be more prone to developing the infection.
Are there any specific conditions that can be mistaken for athlete’s foot?
There are several skin conditions that can be mistaken for athlete’s foot, including eczema, psoriasis, and contact dermatitis. It is important to seek medical advice if you are experiencing persistent symptoms or if you are unsure of the cause of your skin condition.
How can one differentiate between athlete’s foot and other skin conditions caused by mold?
Athlete’s foot is typically characterized by itching, burning, and peeling skin between the toes or on the soles of the feet. Other skin conditions caused by mold may present with similar symptoms, but may also include rashes or bumps on the skin. It is important to seek medical advice if you are experiencing persistent symptoms or if you are unsure of the cause of your skin condition.