Exposure to mold allergens can cause a range of symptoms, from minor irritation to severe respiratory distress. Mold is a type of fungus that thrives in damp environments and can grow in many areas of the home, including bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. While it is impossible to completely eliminate mold from the environment, there are steps that individuals can take to protect their skin from mold allergens and reduce their risk of developing an allergic reaction.

One of the most effective preventive measures is to keep the home clean and dry. Regular cleaning and maintenance can help to reduce the amount of mold spores in the air and prevent the growth of new mold colonies. This includes wiping down surfaces with a disinfectant, using a dehumidifier to reduce moisture levels, and fixing any leaks or water damage as soon as possible. Additionally, individuals with mold allergies should avoid spending time in areas where mold is likely to grow, such as damp basements or poorly ventilated bathrooms.
Key Takeaways
- Keeping the home clean and dry is an effective way to reduce exposure to mold allergens.
- Individuals with mold allergies should avoid spending time in areas where mold is likely to grow.
- If mold is present in the home, it is important to address the issue promptly to prevent further growth and reduce the risk of an allergic reaction.
Understanding Mold and Allergies
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in damp and warm environments. It reproduces by releasing tiny spores into the air, which can cause allergic reactions in some people. Mold spores can be found both indoors and outdoors, and they can enter the body through the nose, mouth, or skin.
Types of Mold
There are many different types of mold, but some of the most common ones that cause allergies include Alternaria, Cladosporium, Aspergillus, and Penicillium. These molds can be found in damp areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements, as well as in outdoor areas such as piles of leaves or compost.
What Causes Mold Allergies?
When mold spores enter the body, the immune system may mistake them for harmful invaders and produce an antibody called immunoglobulin E (IgE). This can cause the release of histamine, which leads to allergy symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and skin rashes.
Allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is a common allergic reaction to mold spores. It can cause symptoms such as nasal congestion, sneezing, and itchy eyes. People with asthma may also experience worsened symptoms when exposed to mold allergens.
Preventive measures such as keeping indoor humidity below 50%, fixing any moisture or water damage in the home, and sleeping with windows closed to keep out outdoor mold can help reduce the risk of mold allergies.
Recognizing Mold Allergy Symptoms
Mold allergies can cause a range of symptoms that can be mild or severe. These symptoms are caused by an allergic reaction to mold spores in the air. Symptoms can vary from person to person, but some of the most common ones include:
Common Symptoms
- Sneezing
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Itchy eyes
- Runny nose
- Shortness of breath
These symptoms are similar to those of hay fever or allergic rhinitis, which is why it can be difficult to distinguish between the two. However, if you experience these symptoms only when you are in a moldy environment, you may have a mold allergy.
Severe Allergic Reactions
In some cases, mold allergies can cause severe allergic reactions. These reactions can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest tightness
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Loss of consciousness
People with asthma are more likely to experience severe allergic reactions to mold. Additionally, people with bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, a lung disease caused by mold spores, may experience chronic coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures

If you suspect that you have a mold allergy, you should consult an allergist or doctor. They will ask you about your symptoms, medical history, and perform a physical exam. They may also recommend diagnostic tests and procedures to confirm the diagnosis.
Skin Prick Test
One of the most common diagnostic tests for mold allergy is a skin prick test. During this test, a small amount of mold allergen is placed on the skin of the forearm or back. The skin is then pricked with a needle to allow the allergen to enter the skin. If you are allergic to the mold, you will develop a raised bump (hive) at the test location on your skin. The size of the bump indicates the severity of your allergy.
Blood Test
A blood test, also known as a radioallergosorbent test (RAST), can also be used to diagnose mold allergy. This test measures the amount of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in your blood. IgE is an antibody that your body produces in response to an allergen. If you are allergic to mold, your blood will contain higher levels of mold-specific IgE antibodies.
Both skin prick and blood tests are reliable and accurate methods for diagnosing mold allergy. Your allergist or doctor will use the results of these tests, along with your medical history and physical exam, to make a diagnosis.
If you are diagnosed with a mold allergy, your allergist or doctor may recommend allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy. Allergy shots can help reduce the severity of your allergy symptoms over time by gradually exposing you to increasing amounts of the allergen.
Preventive Strategies at Home

Mold allergens can cause skin irritation, rashes, and other health problems. Therefore, it is important to take preventive measures to protect your skin from mold allergens. Here are some strategies that can be implemented at home to prevent mold growth and reduce exposure to mold allergens.
Moisture Control
Mold thrives in moist environments. Therefore, it is important to control moisture levels in your home. Keep indoor humidity levels between 30% and 50% by using a dehumidifier or air conditioner. Fix any leaks in pipes, roofs, or windows to prevent water damage. Use ventilation fans in bathrooms and kitchens to reduce humidity levels.
Cleaning Practices
Regular cleaning can help prevent mold growth. Clean and dry any damp or wet surfaces within 24 to 48 hours. Use mold-resistant paint in areas that are prone to moisture, such as bathrooms and basements. Wash bedding, curtains, and other fabrics regularly in hot water to kill mold spores.
Air Filtration Systems
Air filtration systems can help reduce exposure to mold allergens. Use high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters in air purifiers and vacuum cleaners to capture mold spores. Install HEPA filters in your home’s ventilation system to prevent the spread of mold spores.
By implementing these preventive strategies, you can protect your skin from mold allergens and reduce the risk of mold-related health problems.
Medical Management of Mold Allergies
While avoiding mold exposure is the best way to manage mold allergies, medical management can also help alleviate symptoms. Medical management of mold allergies includes medications and allergy shots.
Medications
Antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and decongestants are the most commonly used medications to treat mold allergies. Antihistamines reduce itching, sneezing, and runny nose caused by histamine release. Nasal corticosteroids reduce inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages. Decongestants reduce nasal congestion by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages.
Prescription medications may also be prescribed for severe mold allergies. These medications include leukotriene modifiers, which block the action of leukotrienes, chemicals that cause inflammation in the airways, and immunomodulators, which suppress the immune system.
Allergy Shots and Immunotherapy
Allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy, are a long-term treatment option for mold allergies. Allergy shots contain small amounts of mold allergens, which are injected under the skin. Over time, the body becomes less sensitive to the allergens, and the severity of the allergic reaction decreases.
Immunotherapy is usually recommended for people with severe allergies or those who do not respond well to medications. It is a long-term treatment that can take several months to years to complete.
Lifestyle Modifications

Dietary Considerations
Dietary modifications can play a significant role in reducing the severity of mold allergy symptoms. Individuals with mold allergies should avoid foods that are high in histamine, such as aged cheeses, fermented foods, and alcoholic beverages. These foods can trigger allergic reactions and exacerbate symptoms.
On the other hand, foods that are rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help reduce inflammation and boost the immune system. Foods that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and nuts, can also help reduce inflammation.
Outdoor Activities
Individuals with mold allergies should avoid outdoor activities during rainy or damp weather, as this can increase exposure to outdoor molds. It is also advisable to avoid outdoor activities during periods of high pollen counts, as this can exacerbate allergy symptoms.
When engaging in outdoor activities, individuals with mold allergies should wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, to reduce skin exposure to mold allergens. They should also shower and change clothes immediately after returning indoors to remove any mold spores that may have attached to their clothing or skin.
In conclusion, making simple lifestyle modifications can go a long way in protecting the skin from mold allergens. By avoiding trigger foods and taking precautions during outdoor activities, individuals with mold allergies can reduce the severity of their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Professional Services and Remediation
When it comes to mold remediation, it is always best to seek professional services. A professional mold remediation company can provide a thorough inspection and testing of the affected area to ensure that the mold is properly identified and the extent of the damage is assessed.
Inspection and Testing
During the inspection and testing process, the professionals will use specialized equipment to detect and measure the presence of mold and moisture in the air, walls, and floors. This will help them to determine the type of mold present, the extent of the damage, and the best course of action to take.
If the mold is found to be toxic or harmful, the professionals will take steps to contain the area to prevent the spread of spores. They will also use specialized equipment to remove the mold and restore the area to its original condition.
Mold Removal Techniques
There are several mold removal techniques that professionals use to remove mold from homes and buildings. These techniques include:
-
Dry Ice Blasting: This technique uses dry ice pellets to remove mold from surfaces. The pellets are blasted onto the surface, causing the mold to freeze and become brittle. The mold can then be easily removed without damaging the surface.
-
Chemical Treatment: Chemical treatments are used to kill mold and prevent it from growing back. The chemicals used are safe for humans and pets but are effective at killing mold.
-
HEPA Vacuuming: A HEPA vacuum is used to remove mold spores from the air and surfaces. The vacuum has a filter that traps the spores, preventing them from spreading to other areas.
-
Removal of Contaminated Materials: In some cases, contaminated materials such as drywall and carpets may need to be removed and replaced. This is to ensure that all mold is removed and that the area is safe for occupants.
Overall, professional mold remediation services are necessary when dealing with mold in homes and buildings. They have the experience, knowledge, and equipment needed to properly identify and remove mold, as well as prevent it from returning. It is important to address water damage, humidity, and dampness issues promptly to prevent mold growth and the need for professional remediation services.
Understanding Potential Complications
Mold allergy can cause a variety of complications, ranging from mild to severe. The severity of the symptoms usually depends on the individual’s sensitivity to mold allergens and the duration of exposure.
One of the most common complications of mold allergy is an asthma flare-up. According to the Mayo Clinic, exposure to mold allergens can trigger asthma symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. In some cases, asthma flare-ups can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Another potential complication of mold allergy is fungal sinusitis. Mold spores can enter the nasal cavity and cause inflammation of the sinuses, leading to symptoms such as facial pain, headache, and nasal congestion. Fungal sinusitis can be difficult to treat and may require surgery in severe cases.
In addition to asthma and fungal sinusitis, mold allergy can also increase the risk of infections. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, exposure to mold can weaken the immune system and make individuals more susceptible to infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis.
Overall, it is important to take preventive measures to protect your skin from mold allergens to avoid these potential complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
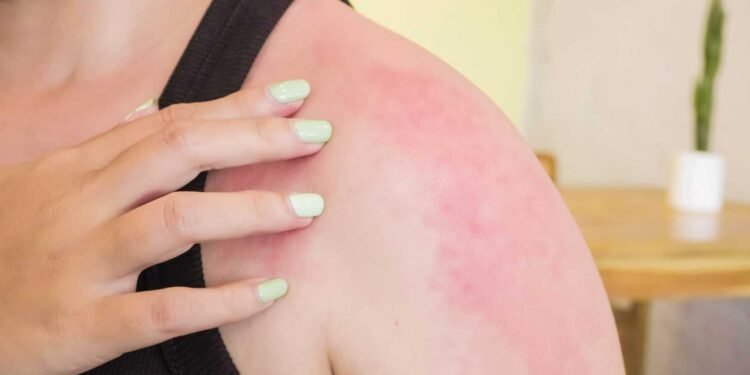
What are the initial signs of skin irritation due to mold exposure?
Skin irritation due to mold exposure can manifest in different ways. The most common symptoms include redness, itching, and a rash. The rash may appear in patches or as raised bumps. In some cases, the rash may be accompanied by blisters or hives. If you suspect that you have been exposed to mold and are experiencing skin irritation, it is important to seek medical attention to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Which over-the-counter medications are effective for skin allergies caused by mold?
Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as cetirizine and loratadine, can be effective in relieving skin allergies caused by mold. These medications work by blocking the effects of histamine, which is released by the body in response to an allergen. Additionally, topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone cream, can help reduce inflammation and itching associated with skin allergies.
How can one identify a skin rash resulting from mold allergens?
A skin rash resulting from mold allergens may appear as red, itchy patches or raised bumps. The rash may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as blisters or hives. If you suspect that you have a skin rash resulting from mold exposure, it is important to seek medical attention to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment.
What self-care strategies can help manage skin allergies to mold?
Self-care strategies that can help manage skin allergies to mold include avoiding exposure to mold, wearing protective clothing when handling moldy materials, and keeping the skin clean and dry. Additionally, applying cool compresses or taking cool baths can help relieve itching and inflammation associated with skin allergies.
What steps can be taken to reduce indoor mold allergen levels?
To reduce indoor mold allergen levels, it is important to identify and address the source of the mold. This may involve repairing leaks, improving ventilation, and reducing humidity levels. Additionally, regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces can help prevent the growth of mold.
Are there specific dietary changes that can help with mold allergies?
While there is no specific diet that can cure mold allergies, some people may find that certain dietary changes can help reduce their symptoms. For example, eating a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, may help reduce inflammation associated with allergies. Additionally, avoiding foods that are high in histamine, such as aged cheeses and fermented foods, may help reduce the severity of allergy symptoms. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes to manage allergies.